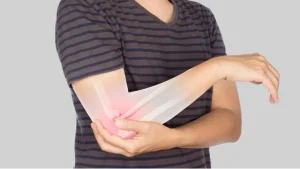

Pain is a normal response of the body to an injury or damage. However, not all pain is the same. There is a difference between chronic and acute pain, and understanding this difference is important for proper treatment and management.
Acute pain is a normal response to a sudden injury or damage, such as a cut, burn, or broken bone. It is a temporary condition that usually goes away within a few days or weeks, as the body heals. Acute pain is usually sharp, and intense, and serves as a warning sign that something is wrong. The body’s natural response to acute pain is to avoid the activity that caused it, and seek treatment if necessary.
Chronic pain, on the other hand, is a long-term condition that lasts for more than three months. Chronic pain is often associated with underlying health conditions, such as arthritis, fibromyalgia, or nerve damage. It can also be the result of an injury that has not fully healed. Chronic pain can persist even after the injury has healed and can be caused by a variety of factors, such as inflammation, nerve damage, or changes in the brain and spinal cord. Unlike acute pain, chronic pain does not serve as a warning sign and does not go away with time.
Chronic pain can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, causing physical and emotional distress. It can limit a person’s ability to perform daily activities and may lead to depression and anxiety. On the other hand, acute pain is usually manageable and treatable and does not typically have a long-lasting impact on a person’s health and well-being.
The treatment for acute and chronic pain is also different. Acute pain is usually treated with over-the-counter pain medication, such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen. Chronic pain, on the other hand, may require more aggressive treatment, such as physical therapy, nerve blocks, or surgery. Chronic pain management often involves a combination of treatments, including medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes, such as regular exercise, healthy eating, and stress management.
In conclusion, understanding the difference between acute and chronic pain is important for proper diagnosis, treatment, and management. Acute pain is a normal response to a sudden injury or damage, while chronic pain is a long-term condition that is often associated with underlying health conditions. The appropriate treatment for each type of pain depends on the cause, duration, and severity of the pain. If you are experiencing chronic pain, it is important to seek the advice of a healthcare professional to determine the best course of treatment.



Stay informed on the newest treatments, technology, and exclusive offers. Subscribe to Ohr Medical’s newsletter with your email address and receive periodic updates without interruption.