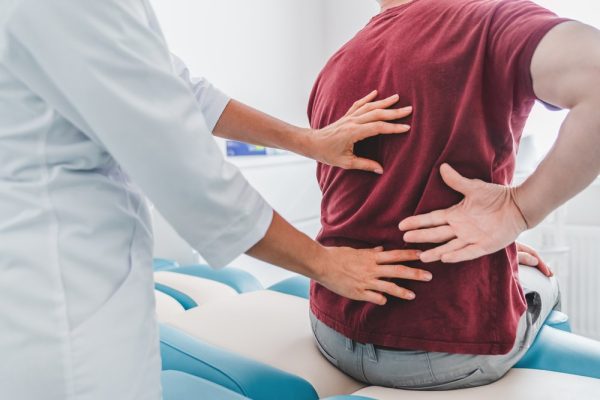

Lower back pain caused by spinal arthritis is a prevalent condition that affects a significant number of individuals. It can cause discomfort, and limited mobility, and impact daily activities. While surgical interventions may be necessary in severe cases, non-surgical back pain management options can effectively alleviate symptoms and improve quality of life.
In this blog, we will explore various non-surgical back pain management strategies, including lifestyle modifications, pain medications, topical back pain treatments, non-invasive therapies, and the role of back pain clinics in providing comprehensive care.
Lower Back Pain Due to Spinal Arthritis
Spinal arthritis, also known as osteoarthritis of the spine or degenerative joint disease, is a condition characterized by the breakdown of the cartilage between the spinal joints. This breakdown leads to bones rubbing against each other, causing inflammation, pain, and stiffness in the lower back. Individuals with spinal arthritis often experience symptoms such as localized pain, limited range of motion, muscle weakness, and radiating pain down the legs.
Managing lower back pain caused by spinal arthritis requires a comprehensive understanding of the condition and its impact on daily life. Seeking appropriate back pain management strategies can help individuals regain control over their symptoms and improve their overall well-being.
Non-surgical Pain Management Options
Lifestyle Modifications
Exercise and Physical Therapy
Regular exercise and targeted physical therapy can play a crucial role in managing lower back pain due to spinal arthritis. Exercise helps strengthen the muscles supporting the spine, improves flexibility, and enhances overall spinal stability.
It is important to consult with a healthcare professional or physical therapist to develop an exercise regimen tailored to individual needs. Examples of exercises beneficial for spinal arthritis include low-impact aerobic activities, core strengthening exercises, and gentle stretching.
Posture and Body Mechanics
Maintaining good posture and practicing proper body mechanics can significantly reduce strain on the lower back. Ergonomic considerations in various activities, such as lifting heavy objects, sitting at a desk, or standing for long periods, can alleviate pain and prevent further damage to the spine.
Simple adjustments, such as using supportive chairs with proper lumbar support, maintaining a neutral spine while lifting, and avoiding prolonged sitting or standing, can make a significant difference in managing lower back pain.
Pain Medications and Topical Back Pain Treatments
Over-the-counter Medications
Over-the-counter pain medications such as NSAIDs, including ibuprofen and naproxen, can provide temporary relief from lower back pain. These medications help reduce inflammation and alleviate pain.
However, it is paramount to follow the recommended dosage and consider any potential side effects or contraindications. It is recommended to consult with a doctor before starting any medication regimen, especially if there are pre-existing medical conditions or concerns about drug interactions.
Prescription Medications
In some cases, prescription medications may be necessary to manage severe lower back pain caused by spinal arthritis. These medications include stronger analgesics, muscle relaxants, or medications targeting nerve pain.
Opioids may be prescribed in specific situations, but their long-term use is generally discouraged due to the risk of dependence and side effects. It is crucial to discuss the potential benefits and risks of these medications with a healthcare professional, considering individual circumstances and medical history.
Topical Back Pain Treatments
Topical creams, ointments, and patches containing analgesic or anti-inflammatory agents can provide localized pain relief. These topical back pain treatments are applied directly to the skin over the affected area.
Common ingredients in these products include menthol, capsaicin, salicylates, or lidocaine. They work by numbing the pain or reducing inflammation. It is important to follow the instructions provided with the product and consult with a healthcare professional if symptoms persist or worsen.
Non-invasive Therapies
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat therapy, using hot packs, heating pads, or warm baths, can help relax muscles and improve blood flow, providing temporary pain relief. The application of heat increases circulation, reduces muscle tension, and promotes relaxation. Cold therapy, using ice packs, cold compresses, or cold baths, can reduce inflammation, numb the affected area, and alleviate pain. Both heat and cold therapy can be used alternatively or as prescribed by a healthcare professional, depending on the individual’s preference and response to back pain treatment.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
TENS is a non-invasive therapy that involves applying low-voltage electrical currents to the skin using electrodes. The electrical stimulation helps disrupt pain signals, stimulates the release of endorphins, and provides relief from lower back pain. TENS units are available for home use, and individuals can receive guidance on proper electrode placement and settings from healthcare professionals or physical therapists.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese medicine technique that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body. It helps restore the balance of energy flow, known as Qi and stimulates the body’s natural healing processes. Some individuals with lower back pain caused by spinal arthritis find acupuncture beneficial in reducing pain and promoting overall well-being. While the exact mechanisms of acupuncture are not fully understood, it may help release endorphins, reduce inflammation, and modulate pain perception.
The Role of a Back Pain Clinic
Back pain clinics specialize in the diagnosis and treatment of various back-related conditions, including lower back pain caused by spinal arthritis. These clinics offer a multidisciplinary approach, bringing together a team of healthcare professionals, including orthopedic specialists, physiotherapists, back pain management experts, and chiropractors. They provide comprehensive care tailored to individual needs, ensuring an accurate diagnosis and personalized treatment plan.
Back pain clinics typically offer diagnostic services, such as imaging tests (X-rays, MRIs) and specialized examinations, to identify the underlying causes of lower back pain. Through a collaborative approach, healthcare professionals work together to come up with a comprehensive treatment plan that could include a combination of back pain management techniques.
These may involve medication management, physical therapy, spinal manipulation, injections (such as epidural injections or facet joint injections), and regenerative therapies (such as platelet-rich plasma or stem cell therapy). Additionally, back pain clinics may offer educational resources, rehabilitation programs, and counseling services to empower individuals in managing their condition effectively.
Conclusion
Lower back pain due to spinal arthritis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, but it can be effectively managed through non-surgical approaches. By implementing lifestyle modifications, utilizing pain medications and topical treatments, exploring non-invasive therapies, and seeking specialized care from a back pain clinic, individuals can find relief and regain control over their symptoms.
It is essential to consult with healthcare professionals, follow their guidance, and tailor treatment plans to individual needs. With the right approach, effective pain management is possible, leading to improved well-being and a better quality of life for individuals dealing with spinal arthritis-related lower back pain.



Stay informed on the newest treatments, technology, and exclusive offers. Subscribe to Ohr Medical’s newsletter with your email address and receive periodic updates without interruption.